陈小林课题组发表植物病原真菌和细菌翻译后修饰研究综述文章
南湖新闻网讯(通讯员 刘彩云)近日,我校植物科学技术学院、农业微生物学国家重点实验室陈小林课题组与合作者发表综述文章,综述对翻译后修饰调控植物病原真菌和细菌生物学过程和致病过程的调控机制相关进展进行了系统的总结。
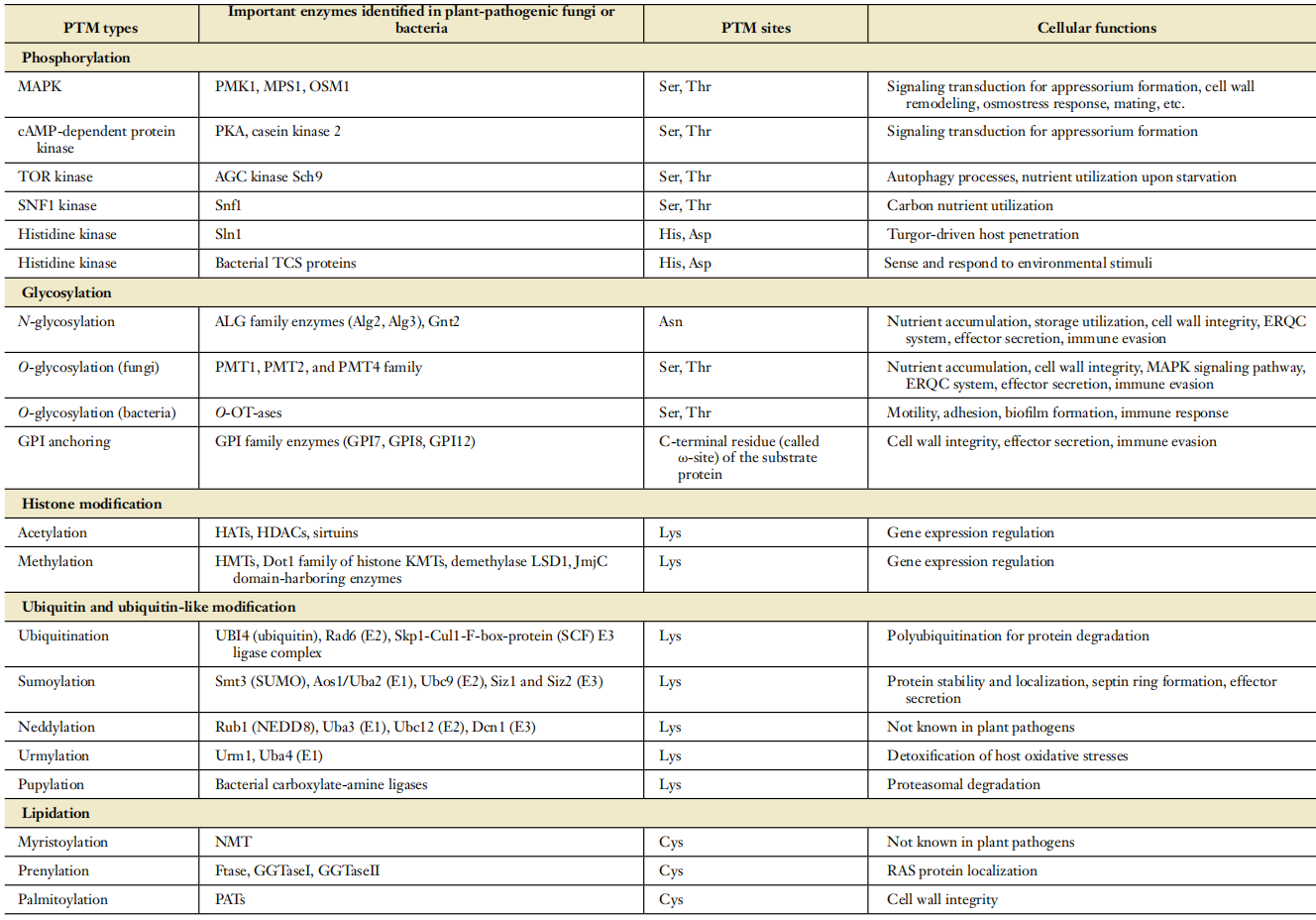
Types of posttranslational modifications (pTMs) in plant-pathogenic fungi or bacteria
植物病原菌(包括真菌和细菌)的生长发育,环境响应以及侵染过程是如何被精确调控的,是一个非常复杂的问题。关于转录水平的调控在真菌和细菌的发育和侵染中的重要作用已经被广泛深入的解析,而蛋白质翻译后修饰(pTMs)层面的调控同样在植物病原菌致病过程中发挥着关键作用,但受到的关注相对较少。长期以来,对真菌和细菌感染过程中pTMs的研究集中在磷酸化的作用,特别是在侵染结构形成过程中涉及的信号通路(如cAMp和MApKs信号通路)。
近十年来,关于翻译后修饰调控植物病原真菌和细菌生物学过程和致病过程的调控机制研究取得了一些重要的进展,本综述对该领域的相关进展进行了系统的总结(主要内容包括磷酸化修饰,糖基化修饰,组蛋白修饰,泛素化和类泛素化修饰,脂质修饰,氧化还原修饰等),归纳了翻译后修饰研究的主要策略和方法,探讨了翻译后修饰研究与病害防控的关系,同时对未来植物病原菌翻译后修饰领域的研究趋势进行了展望。
审核人:陈小林
【英文摘要】
posttranslational modifications (pTMs) play crucial roles in regulating protein function and thereby control many cellular processes and biological phenotypes in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Several recent studies illustrate how plant fungal and bacterial pathogens use these pTMs to facilitate development, stress response, and host infection. In this review, we discuss pTMs that have key roles in the biological and infection processes of plant-pathogenic fungi and bacteria. The emerging roles of pTMs during pathogen–plant interactions are highlighted. We also summarize traditional tools and emerging proteomics approaches for pTM research. These discoveries open new avenues for investigating the fundamental infection mechanisms of plant pathogens and the discovery of novel strategies for plant disease control.
论文链接:https://www.annualreviews.org/doi/10.1146/annurev-phyto-021320-010948






























