油菜团队揭示植物缺磷条件下膜脂重塑机制
南湖新闻网讯(通讯员 杨报)近日,我校油菜团队首次发现了植物鞘磷脂GIpC可以被NpC4水解,揭示了NpC4介导的植物膜脂重塑新机制。
磷是植物生长发育所必需的一种大量元素,植物对磷素的有效性利用是提高植物产量的关键。细胞内大量的磷素用于细胞膜磷脂的合成,细胞膜磷脂是细胞内磷素的储存库。植物在缺磷条件下,膜磷脂会被磷脂酶水解释放出磷素供其他必需含磷物质(如DNA、RNA、ATp和蛋白质等)的合成,植物通过该机制适应磷素的缺乏,这一代谢过程通过多个关键磷脂酶完成。
非特异性磷脂酶C4(NpC4)是植物NpC家族中活性最强的,在缺磷条件下被诱导表达最高的一个基因。NpC4在植物缺磷条件下的代谢功能尚不清楚,解析NpC4代谢功能的分子生化机制对植物磷素的高效利用意义重大。
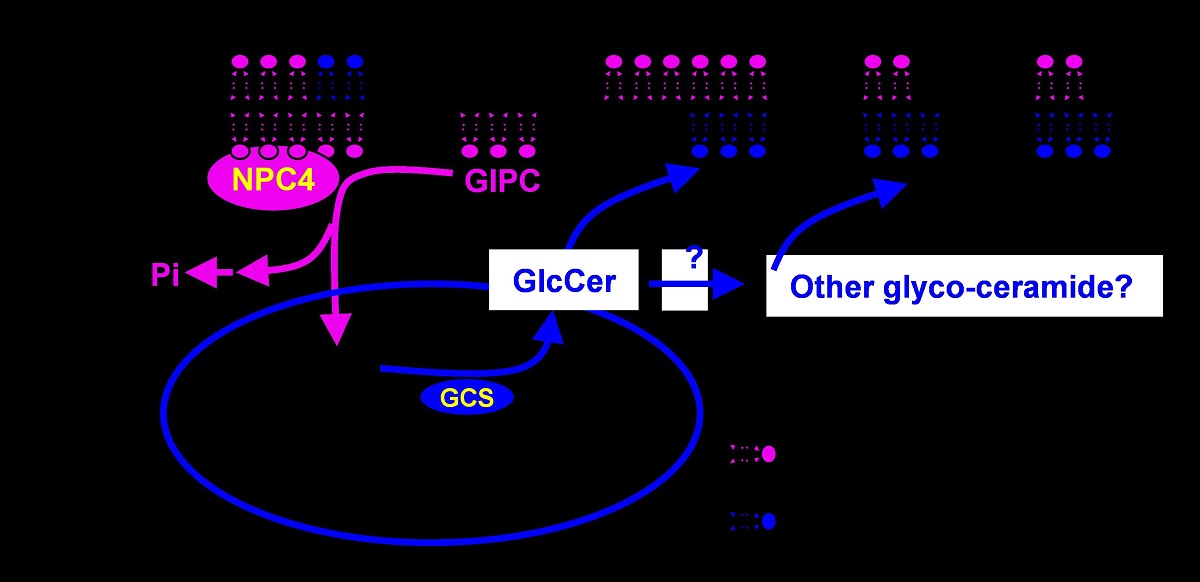
在该研究中,研究者通过扩大拟南芥缺磷条件下脂质组的检测,发现植物特有的鞘磷脂糖基肌醇磷酸神经酰胺(glycosyl inositol phosphoryl ceramide,GIpC)在缺磷条件下会显著下降,同时根中鞘糖脂葡萄糖神经酰胺(glucosylceramide,GlcCer)会大幅度上升。研究者检测了缺磷条件下npc4体内的鞘脂变化情况,发现与野生型(WT)相比,缺磷条件下npc4中GIpC的含量显著高于WT,同时GlcCer的含量则显著低于WT,缺磷条件下NpC4的缺失导致鞘脂代谢受阻。研究者进一步通过体外酶活实验分析发现NpC4可将GIpC水解形成羟基神经酰胺(hydroxyceramide,hCer)和带磷酸基团的极性头部。基因表达分析表明拟南芥在缺磷条件下NpC4和GCS(glucosylceramide synthase,葡萄糖神经酰胺合成酶)会被大量诱导表达,诱导的GCS将NpC4水解GIpC生成的hCer转化为GlcCer。这些研究结果表明NpC4水解GIpC,介导了缺磷条件下鞘磷脂到鞘糖脂的转化。
GIpC是植物特有的一种鞘脂,含量占鞘脂总量的60%以上。GIpC是植物细胞膜的重要组成部分,通常与固醇和跨膜蛋白等形成细胞膜上特殊的抗去污剂结构-脂筏,在植物细胞对外界信号响应上发挥着重要作用。亚细胞定位结果证明NpC4定位于细胞质膜(pM),同时可在细胞膜蛋白提取物抗去污剂组分中检测到NpC4-GFp,将分离的细胞质膜蛋白通过蔗糖梯度离心分离,可在脂筏组分中检测到NpC4-GFp。同时脂质分析发现NpC4-GFp可与GIpC共定位,进一步证明了脂筏定位的NpC4可通过水解脂筏中的GIpC使细胞适应缺磷胁迫。
英文摘要(Abstract)
phosphate is a vital macronutrient for plant growth, and itsavailabilityin soil is critical for agricultural sustainability and productivity.Asubstantial amount of cellular phosphate is used to synthesize phospholipidsforcell membranes. Here we identify a key enzyme, nonspecific phospholipaseC4(NpC4), that is involved in phosphosphingolipid hydrolysis and remodelinginArabidopsis during phosphate starvation. The levelofglycosylinositolphosphorylceramide (GIpC), the most abundant sphingolipid inArabidopsis thaliana, decreasedupon phosphate starvation. NpC4was highlyinduced by phosphate deficiency, and NpC4 knockouts in Arabidopsis decreasedthe loss ofGIpC and impeded root growth during phosphate starvation. Enzymaticanalysisshowed that NpC4 hydrolyzed GIpC and displayed a higher activity towardGIpC asa substrate than toward the common glycerophospholipidphosphatidylcholine.NpC4 was associated with the plasma membrane lipid rafts inwhich GIpC ishighly enriched. These results indicate that NpC4 uses GIpC as asubstrate inplanta and the NpC4-mediated sphingolipid remodeling plays apositive role inroot growth in Arabidopsis response to phosphate deficiency.
论文链接:https://academic.oup.com/plcell/advance-article/doi/10.1093/plcell/koaa054/6094430
相关评论链接:https://academic.oup.com/plcell/advance-article/doi/10.1093/plcell/koaa057/6094428
审核人:郭亮






























